This post may contain affiliate links which means I may receive a commission for purchases made through links. Learn more about policies on my about page.
Table of Contents
Understanding Subcutaneous Fat: Definition, Location, and Health Implications
Subcutaneous fat, also known as subcutaneous adipose tissue, is the layer of fat located directly beneath the skin. It serves as a crucial energy reserve and provides insulation and protection for the body. Understanding the definition and characteristics of subcutaneous fat is essential in comprehending its role in overall health and wellness. In this blog post, we will delve into the specifics of subcutaneous fat, its distribution in the body, and its significance in relation to health and aesthetics.
What is Subcutaneous Fat?
Subcutaneous fat is the fat that is stored directly beneath the skin. It is the most visible type of fat and is found throughout the entire body, covering the surface of the skin. This type of fat acts as a crucial energy reserve and provides insulation, helping to regulate body temperature.
Definition
Subcutaneous fat is the layer of fat tissue located under the dermis, or skin. It serves as a protective cushion for the body, and also helps to store and release energy.
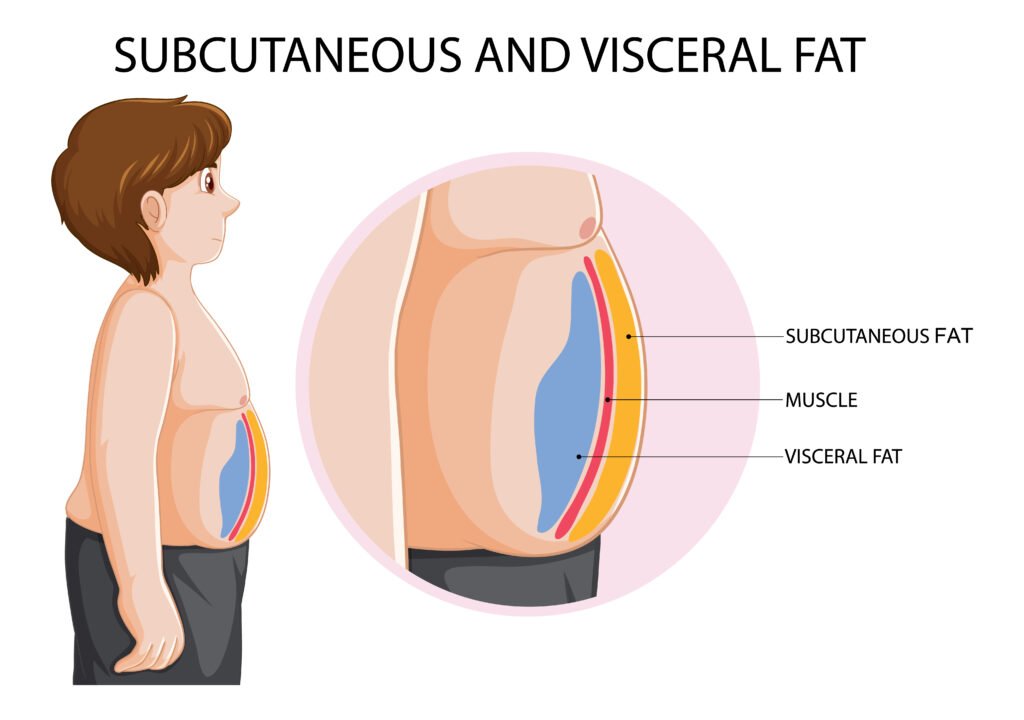
Location in the Body
Subcutaneous fat is distributed across the entire body, with higher concentrations in areas such as the abdomen, thighs, hips, and buttocks. It is also found in lower amounts in the arms, back, and other regions.
For more detailed information about subcutaneous fat, you can refer to this resource on Mayo Clinic to better understand its significance in the body.
Functions of Subcutaneous Fat
Subcutaneous fat, found beneath the skin, plays significant roles in the body.
Energy Storage
Subcutaneous fat serves as a crucial energy reserve. When the body requires additional energy due to decreased food intake or increased energy expenditure, this fat provides a readily available source of fuel. It offers a buffer against starvation and is vital for ongoing energy demands.
Insulation
Serving as an insulating layer, subcutaneous fat helps maintain body temperature. It acts as a thermal barrier, protecting the body from cold temperatures by retaining heat and preventing heat loss.
Temperature Regulation
In regulating body temperature, subcutaneous fat aids in maintaining homeostasis. It prevents extremes in body temperature, ensuring the body functions optimally across varying environmental conditions.
In addition to its aesthetic role, subcutaneous fat performs crucial functions that are essential for overall health and well-being. Understanding these functions provides valuable insight into the significance of subcutaneous fat in the body’s physiological processes.
Health Implications of Subcutaneous Fat
Healthy Levels
Maintaining a healthy level of subcutaneous fat is essential for overall well-being. Subcutaneous fat serves as a protective layer, insulating the body and regulating temperature. It also acts as a reserve energy source, providing fuel during times of need. Healthy levels of subcutaneous fat vary depending on age, gender, and body type. For men, a healthy range is typically between 18-24%, while for women, it is between 25-31%. These percentages ensure that the body has an adequate level of stored energy while mitigating the risks associated with excess fat accumulation.
Risks of Excess Subcutaneous Fat
Excess subcutaneous fat can lead to various health risks, including cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and hypertension. When the body accumulates an excessive amount of subcutaneous fat, it can lead to obesity, which puts additional stress on the heart and other vital organs. Furthermore, excess subcutaneous fat can contribute to insulin resistance, disrupting the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar levels. This increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Additionally, the release of inflammatory substances from excess fat cells can lead to chronic low-grade inflammation, further raising the risk of developing cardiovascular problems. It is crucial to maintain a balance and healthy level of subcutaneous fat to reduce the risk of these health complications.
For more information on healthy levels of subcutaneous fat and the risks of excess subcutaneous fat, refer to the detailed resources provided by the World Health Organization and the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
Measuring Subcutaneous Fat
Body Mass Index (BMI)
To measure subcutaneous fat, one popular method is through the calculation of Body Mass Index (BMI). BMI is determined by dividing a person’s weight in kilograms by the square of their height in meters. This measurement indicates the level of body fat based on an individual’s weight and height. While it’s a simple and quick method, it does have limitations, especially when it comes to differentiating between fat and muscle.
Body fat scales paired up with the Renpho app for smartphone will measure BMI and subcutaneous fat every time you step on them.
Waist Circumference
Another way to assess subcutaneous fat is by measuring waist circumference. Research has shown that excess fat around the abdomen can be a risk factor for various health issues. For men, a waist circumference of over 40 inches and for women, over 35 inches, may indicate a higher level of subcutaneous fat and an increased risk of health problems.
Skinfold Thickness
Measuring skinfold thickness is another method used to estimate subcutaneous fat. This involves using calipers to measure the thickness of a fold of skin at various points on the body. These measurements can then be used to calculate the percentage of body fat. While this method can be subjective based on the skill of the person taking the measurements, it can provide a more direct assessment of subcutaneous fat in specific areas of the body.
When it comes to measuring subcutaneous fat, employing a combination of these methods can provide a more comprehensive understanding of an individual’s body composition. It’s essential to remember that these measurements should be part of a broader assessment of overall health and not the sole focus. Always consult with a healthcare professional for a complete evaluation.
For further information on the importance of measuring subcutaneous fat, refer to the National Health Service.
Tips for Managing Subcutaneous Fat
Balanced Diet
Maintaining a balanced diet is crucial for managing subcutaneous fat. Focus on incorporating a variety of nutrient-dense foods such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Opt for foods high in fiber to promote a feeling of fullness and aid in weight management. Additionally, limit the consumption of processed foods, sugary snacks, and high-calorie beverages, as they can contribute to the accumulation of subcutaneous fat. For further details on creating a balanced diet, you can refer to the NHS website.
Regular Exercise
Engaging in regular physical activity is essential for reducing subcutaneous fat. Incorporate a combination of cardiovascular exercises, such as brisk walking or cycling, and strength training to promote fat burning and muscle building. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, as recommended by the World Health Organization. This not only aids in reducing subcutaneous fat but also improves overall health and fitness levels.
Stress Management
Effective stress management plays a significant role in managing subcutaneous fat. High stress levels can lead to the release of cortisol, a hormone that promotes the storage of fat, particularly in the abdominal area. To mitigate stress, consider incorporating relaxation techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or engaging in hobbies. Prioritising quality sleep and maintaining a healthy work-life balance can also aid in stress reduction. For further information on stress management, visit the Mind website.
Conclusion
In conclusion, subcutaneous fat is the layer of fat located just beneath the skin. It plays a crucial role in regulating body temperature, storing energy, and providing cushioning and insulation. Understanding the impact of subcutaneous fat on overall health is essential for making informed lifestyle choices and maintaining a healthy body composition. By prioritising a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and other healthy habits, individuals can effectively manage subcutaneous fat levels and promote optimal well-being.